5 Rate Limiting Strategies Explained Simply
You are now 171,001+ subscribers strong. Let’s try to reach 172k subscribers by 20 September. Share this post & I'll send you some rewards for the referrals. Get my system design playbook for FREE on newsletter signup: This post outlines important rate limiting strategies. You will find references at the bottom of this page if you want to go deeper.
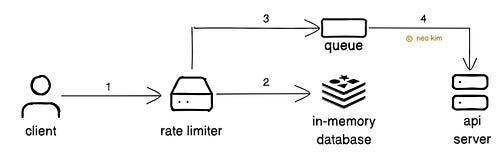
Once upon a time, there was a tiny bank. They had only a few customers. And offered services through a mobile app. Yet some people attempted to log in to customers’ accounts by guessing passwords. So they solved this problem by blocking specific IP addresses using firewall rules. But one day, their app became extremely popular. And it became difficult to block many malicious IP addresses quickly. So they set up request throttling. It means slowing down requests instead of blocking them. Yet it doesn’t stop abuse because someone could queue many requests and waste resources. So they installed a rate limiter. Rate limiting means controlling the number of requests a user can make within a time window. For example, their app allows only 5 login attempts an hour by a user. While future attempts of the user get blocked until the time window passes. This technique prevents abuse and server overload. Imagine rate limiting as tickets to a movie theater. A show sells only 50 tickets. Once the tickets are sold, you’ve got to wait for the next showtime to get in. Here’s how it works:
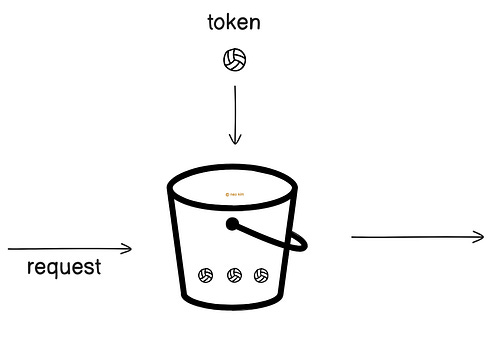
Onward. Vapi x MiniMax Free TTS API Week - SponsorVapi is partnering with MiniMax for a free TTS API week. Developers & builders can get: • Free & unlimited access to all MiniMax voices until Sept 22 • 20% off MiniMax API for a year if you try it this week • $10 Vapi credit with code VAPIMINIMAX10 Explore next-gen TTS with the free API now. Rate LimitingThere are different strategies to implement a rate limiter. Let’s dive in: 1. Token BucketIt’s one of the most popular rate limiting strategies. And here’s how it works:
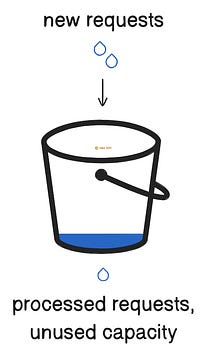
This strategy is easy to implement and understand. Also it allows spiky traffic. For example, imagine the bucket has 5 tokens and refills at 1 token per hour. A user can make 5 requests in a few seconds, but then they’d have to wait 1 hour to make an extra request. Yet this strategy affects the user experience by making them wait a long time if new tokens get added slowly. While refilling tokens quickly might affect the security. So it’s necessary to control the speed at which tokens get added based on the domain and server capacity. 2. Leaky BucketThis strategy ensures fair usage of resources by smoothing traffic. Here’s how it works:
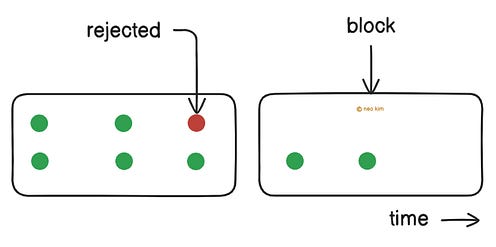
Yet unused capacity gets lost even without processing requests with this approach. Besides it’ll block requests during a traffic burst. So use this strategy when traffic is predictable, and when it’s okay to block some requests for users during a traffic burst. Ready for the next technique? 3. Fixed WindowThis strategy works well with predictable traffic. Here’s how:
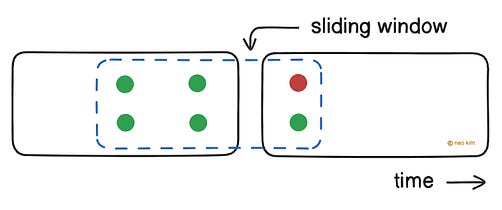
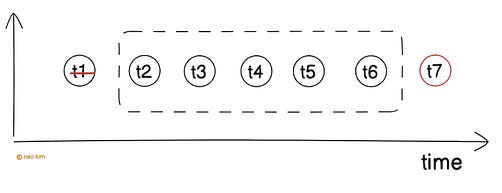
Although it’s easy to implement, it allows traffic bursts on window boundaries. For example, a user could double their allowed requests by sending them at the end of one window and the start of the next. Thus overloading the server. So use this strategy when the server can handle occasional traffic bursts. Let’s keep going! 4. Sliding Window CounterThis strategy offers fairness and works better with traffic bursts. Here’s how:
Put simply, it approximates the number of requests within the last hour from the current time. Yet it’s more complex to implement than the fixed window, and the rate limiter count is approximate. So use this strategy to rate limit efficiently in systems with moderate traffic. 5. Sliding Window LogIt’s like the sliding window counter, except it keeps a log of all request timestamps. Thus offering accuracy. Here’s how it works:
This strategy is precise and fair. Yet it’s memory and CPU-intensive. So use it only when strict precision and fairness are necessary. A rate limiter protects infrastructure from abuse and ensures high availability. Yet it’s necessary to choose the right rate limiting strategy to avoid blocking users unnecessarily. Also users from a building might share the same IP address. So it’s better to rate limit a person using an API key instead of their IP address for accuracy and fairness. The right strategy for rate limiting depends on simplicity and the fairness needs. A banking app needs precision and fairness. So it’s better to use the sliding window log strategy for it. Subscribe to get simplified case studies delivered straight to your inbox: Want to advertise in this newsletter? 📰 If your company wants to reach a 170K+ tech audience, advertise with me. Thank you for supporting this newsletter. You are now 171,001+ readers strong, very close to 172k. Let’s try to get 172k readers by 20 September. Consider sharing this post with your friends and get rewards. Y’all are the best. ReferencesUnlock access to every deep dive article by becoming a paid subscriber: |