7 Best Practices For Api Design
You are now 171,001+ subscribers strong. Let’s try to reach 172k subscribers by 10 September. Share this post & I'll send you some rewards for the referrals. Get my system design playbook for FREE on newsletter signup: This post outlines best practices for API design. You will find references at the bottom of this page if you want to go deeper.
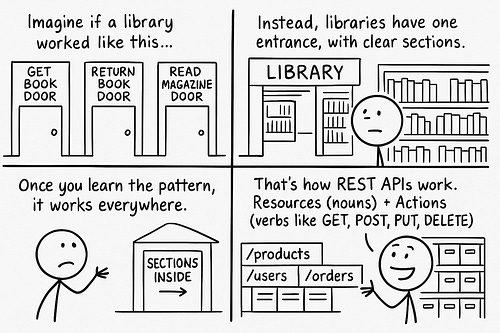
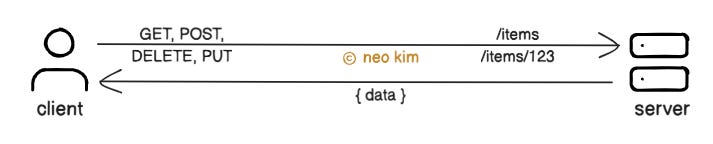
Once upon a time, there was a tiny startup. They had only a few customers. So they ran their site using a simple monolith architecture. But one day, their site became extremely popular. So they set up a microservices architecture for scalability. Yet they didn’t know much about API design. And their public APIs often failed from spiky traffic. Also they sent the entire dataset when users asked for just the latest data. Besides it became difficult to manage APIs as they added more features. So they decided to study the best practices to design APIs. Onward. Design, Animate, Publish—All in Framer (Sponsor)Still using a copy-paste website? Framer is the design-first, no-code website builder that lets anyone ship a production-ready site in minutes. Whether you’re starting with a template or a blank canvas, Framer gives you total creative control—no coding required. Add animations, localize with one click, and collaborate in real-time with your whole team. You can even A/B test and track clicks with built-in analytics. Ready to build a site that looks hand-coded—without hiring a developer? Launch your site for free at Framer dot com, and use code SYSTEMDESIGN for a free month on Framer Pro. Best Practices for API DesignHere’s what they learned: 1. REST FundamentalsREST stands for Representational State Transfer. It's an architectural pattern for systems to talk with each other over the Internet. It helps to organize the data simply and clearly. Think of REST like a book library. There is just one entrance to borrow or return books. While books get organized into different sections by subject. REST APIs organize data into resources similarly. Here’s how it works:
This approach makes the APIs predictable and easy to interact with. Yet it might be limiting for some real-world actions, such as publishing a draft of a document. So it’s necessary to have a balance between REST principles and a pragmatic approach. Let’s keep going! 2. Error HandlingA status code tells the client whether a request succeeded or failed. API Error handling means returning clear, consistent error messages if something goes wrong. Thus making it easy for the client to handle the error properly. Imagine you’re at an airport. A bad API error is like the departure board displaying random errors when flight time changes. It doesn’t tell you which flight, why, or what to do next. While a good API error is like displaying the flight name and its reason behind time changes. Here’s how it works:
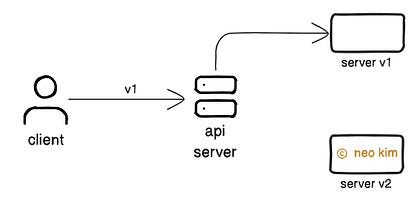
Proper error handling in APIs makes a site reliable. Yet it needs extra effort and discipline to handle each failure scenario. Besides error message must include only enough information to avoid security risks. Ready for the next technique? 3. API VersioningIt’s necessary to version an API so new changes don’t break existing clients. Think of API versioning like publishing a new book edition. The old book copies that have already been sold don’t get updated. But the new edition gets released with improvements. So readers who need the updates can get the latest edition. And those using the old one can read it without issues. Here’s how it works:
Thus ensuring backward compatibility. Here are 2 alternative approaches to implement API versioning:
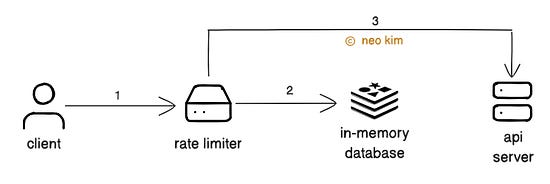
But query parameters are designed for filtering or searching data. So it's better to avoid them for versioning. API versioning makes a site reliable. Yet it increases the complexity and maintenance efforts. So use it only for breaking changes. 4. Rate LimitingRate limiting means controlling the number of requests a client can make to an API within a period. It prevents server overload and protects the API from abuse. Imagine rate limiting as telling a person how many things they can have during a giveaway. Here’s how it works:
The API includes special HTTP headers in the response about the rate-limiting rules. Here are some of them:
While the API returns a Rate limits ensure the high availability of a site. But it’s necessary to set a reasonable rate limit for a better user experience. Besides many people might share the same IP address. So it’s better to rate limit a person using an API key instead of their IP address for accuracy and fairness. Ready for the best part? 5. PaginationAPI pagination is the technique of breaking a large dataset into smaller chunks. It lets the client request data in smaller parts instead of all at once. Thus achieving low latency and reduced bandwidth usage. Imagine a big book with 1,000 pages. Pagination is like reading through it one page at a time, instead of all at once. There are 2 ways to implement pagination: Offset Pagination It’s the most common technique for interacting with a dataset in pages. Here’s how it works:
Offset pagination is simple to understand and easy to implement. Also it lets the client access random pages. But it’s slow with large datasets because the database scans the skipped records as well. Besides there’s a risk of inconsistent results if data gets added or removed during paging. Cursor Pagination It uses a pointer (cursor) to a specific record in the dataset. It means the server returns results after the cursor instead of skipping records. Here’s how it works:
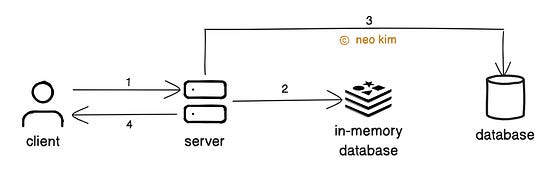
Cursor pagination doesn't scan skipped records; instead, it uses the database index. Thus making it efficient for large datasets. Also it gives consistent results even if data gets added or removed during paging. But it’s complex to implement and doesn’t support navigation to a specific page. So choose the pagination technique based on the data size and data update frequency. Ready for the best technique? 6. IdempotencyIdempotency means processing a request only once to avoid unwanted side effects. Imagine paying for something online. And mistakenly getting charged twice for the same transaction. An idempotent API prevents this problem. Here’s how it works:
And the in-memory database gets queried to check if a future request has been processed already. Also the client generates a new UUID whenever the request payload changes. Thus ensuring only new requests get processed. Here are 2 alternative approaches to implement idempotency:
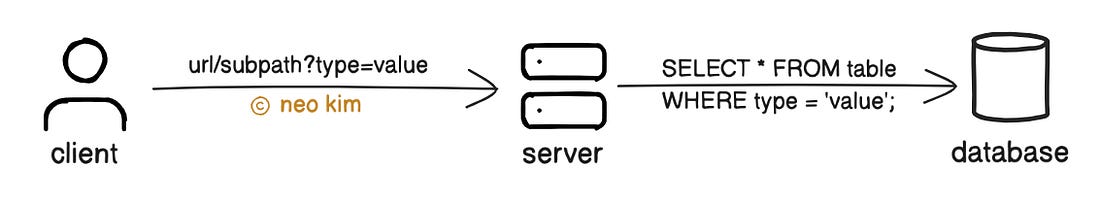
Idempotency is essential for building reliable APIs. Yet it increases the complexity and operational costs. Besides the idempotency keys should be removed periodically to reduce memory usage. So use it mainly for critical APIs where retries could cause unwanted side effects. 7. Filtering and SortingAPI filtering means returning results that match specific conditions in request parameters. Here’s how it works:
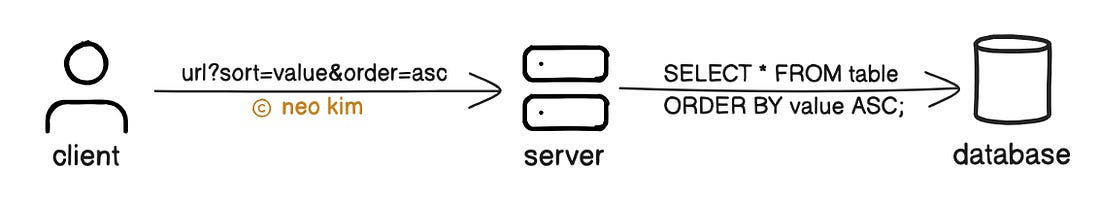
Filtering improves performance by reducing bandwidth usage. But it increases the complexity of server logic. So use it only if specific data from a large dataset is needed. API sorting means ordering the results by a specific field, using request parameters. Here’s how it works:
Sorting improves usability by ordering data. But it might slow down queries on large datasets without indexes. So use it only if ordering is important. The internet runs using APIs. While good APIs are consistent, predictable, and designed to scale without problems. So it's necessary to have clear documentation, useful error messages, and proper monitoring for APIs. Subscribe to get simplified case studies delivered straight to your inbox: Want to advertise in this newsletter? 📰 If your company wants to reach a 170K+ tech audience, advertise with me. Thank you for supporting this newsletter. You are now 171,001+ readers strong, very close to 172k. Let’s try to get 172k readers by 10 September. Consider sharing this post with your friends and get rewards. Y’all are the best. References
Unlock access to every deep dive article by becoming a paid subscriber: |